Re-use of this resource is governed by a Creative Commons
Attribution-
NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Tensile test for metals and alloys
Select the materials
to test in a tensometer:
Approximately pure aluminium.
Approximately pure copper.
Cu-46 wt% Zn α-β brass.
Fe-C alloy with lower carbon content.
Fe-C alloy with higher carbon content.
Made from silver steel annealed at 750 ℃ and rapidly quenched in water.
18.7-Cr, 70.1-Fe, 11.1-Ni wt% alloy.
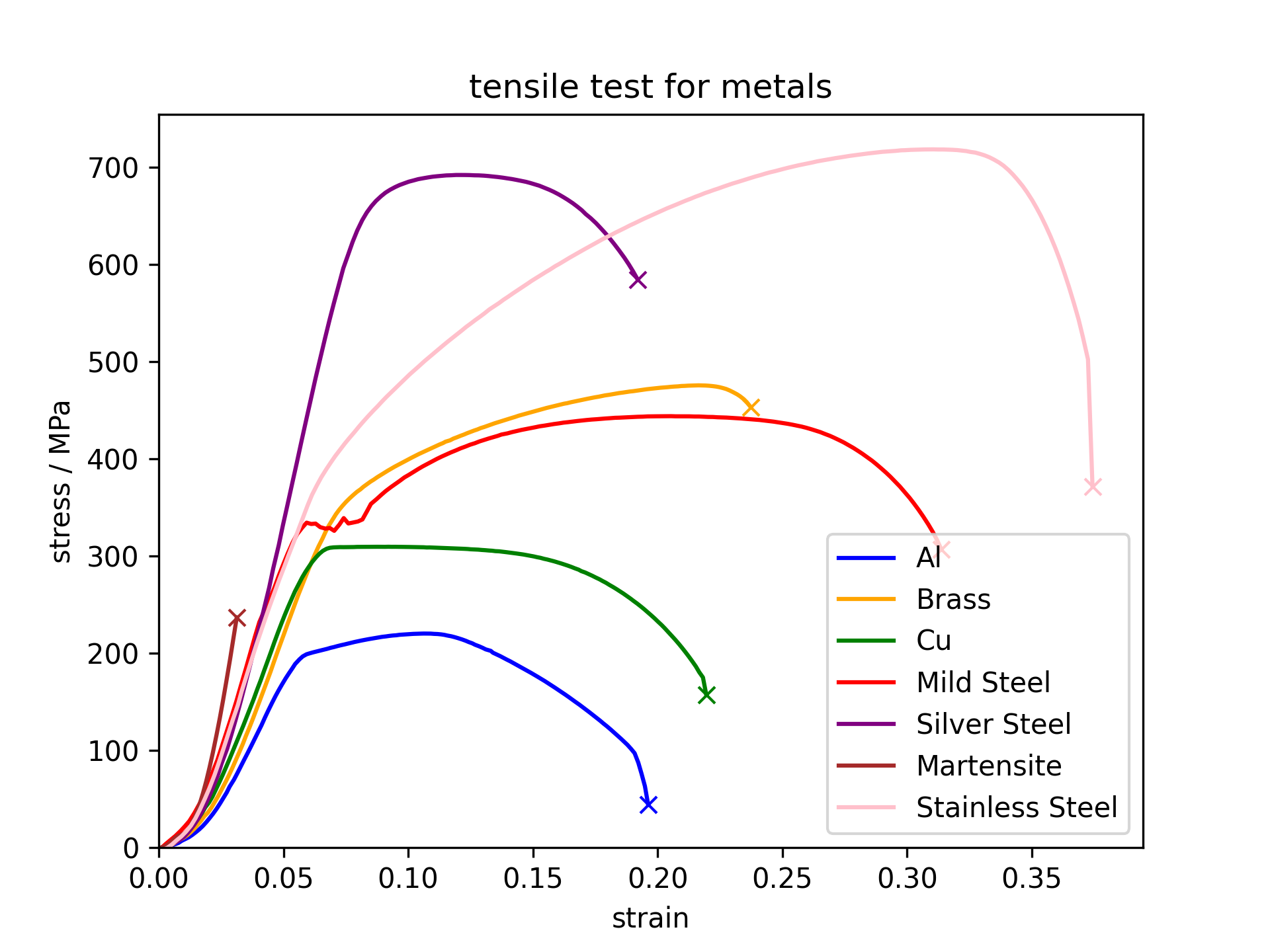
A summary to compare the mechanical behaviour of the metallic materials above.
Approximately pure aluminium.
Approximately pure copper.
Cu-46 wt% Zn α-β brass.
Fe-C alloy with lower carbon content.
Fe-C alloy with higher carbon content.
Made from silver steel annealed at 750 ℃ and rapidly quenched in water.
18.7-Cr, 70.1-Fe, 11.1-Ni wt% alloy.
A summary to compare the mechanical behaviour of the metallic materials above.
Tensile test for aluminium
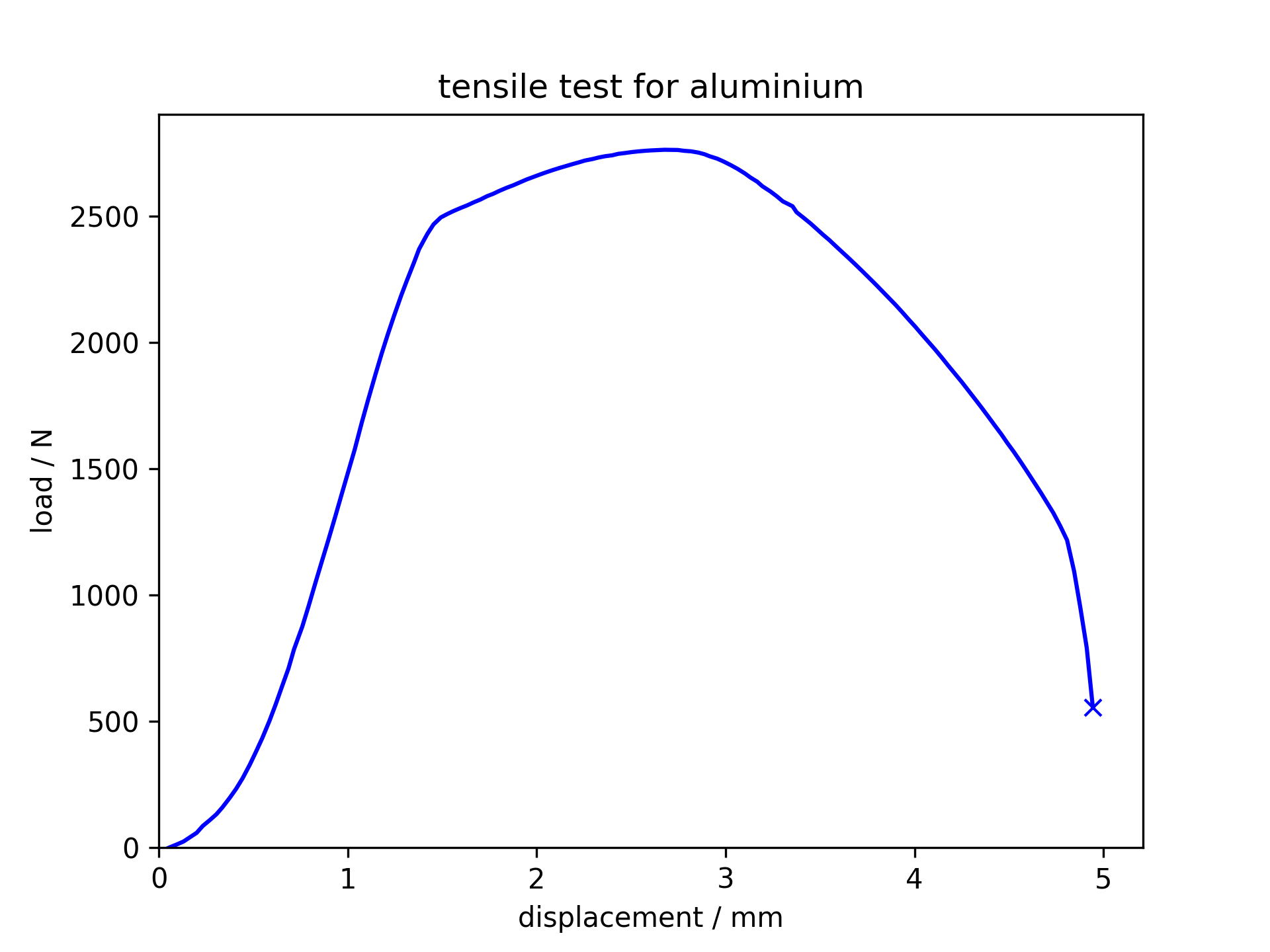
Aluminium is ductile and necks before fracture.
Tensile test for copper
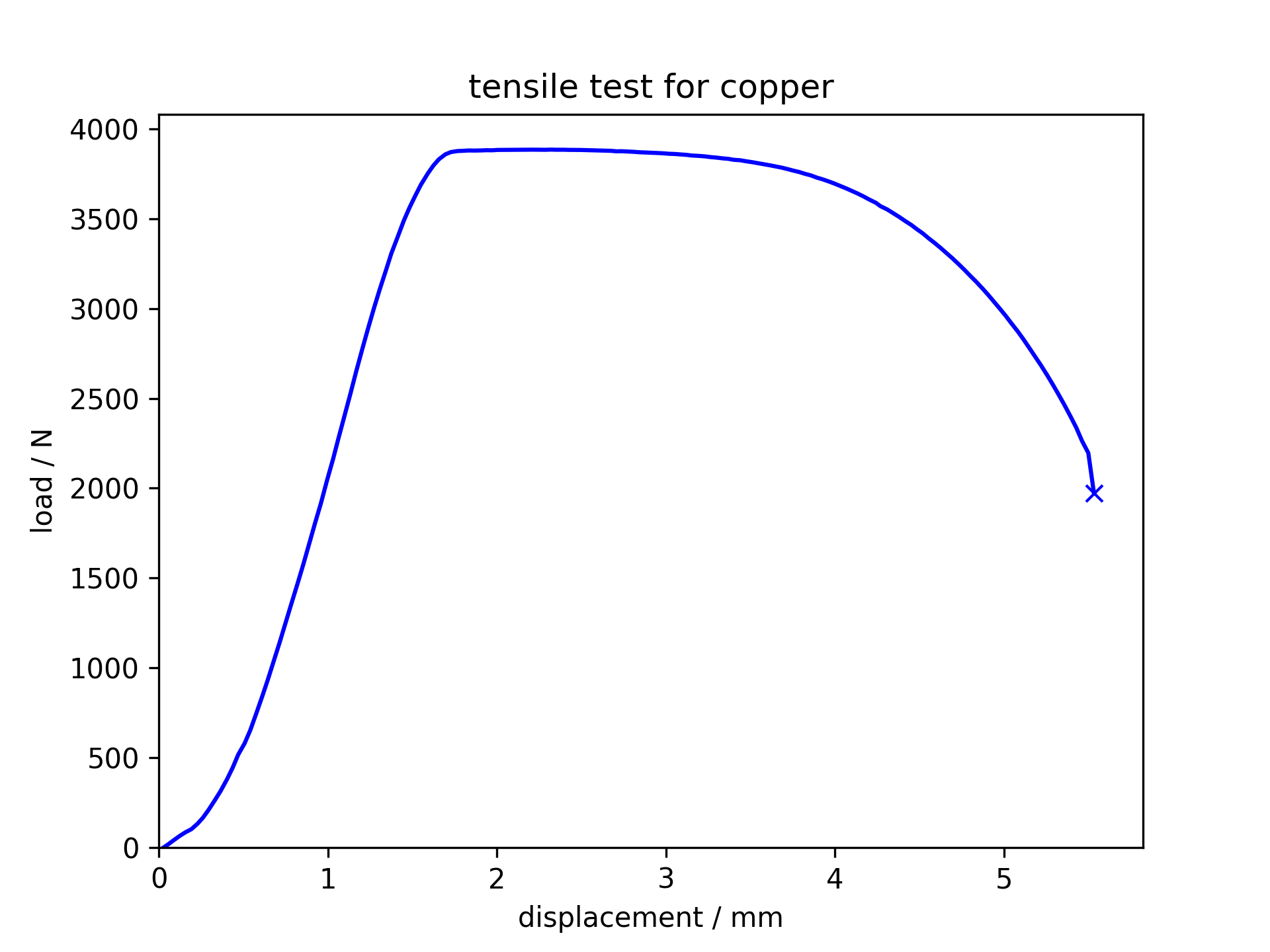
Copper is ductile
and necks before fracture.
Tensile test for brass
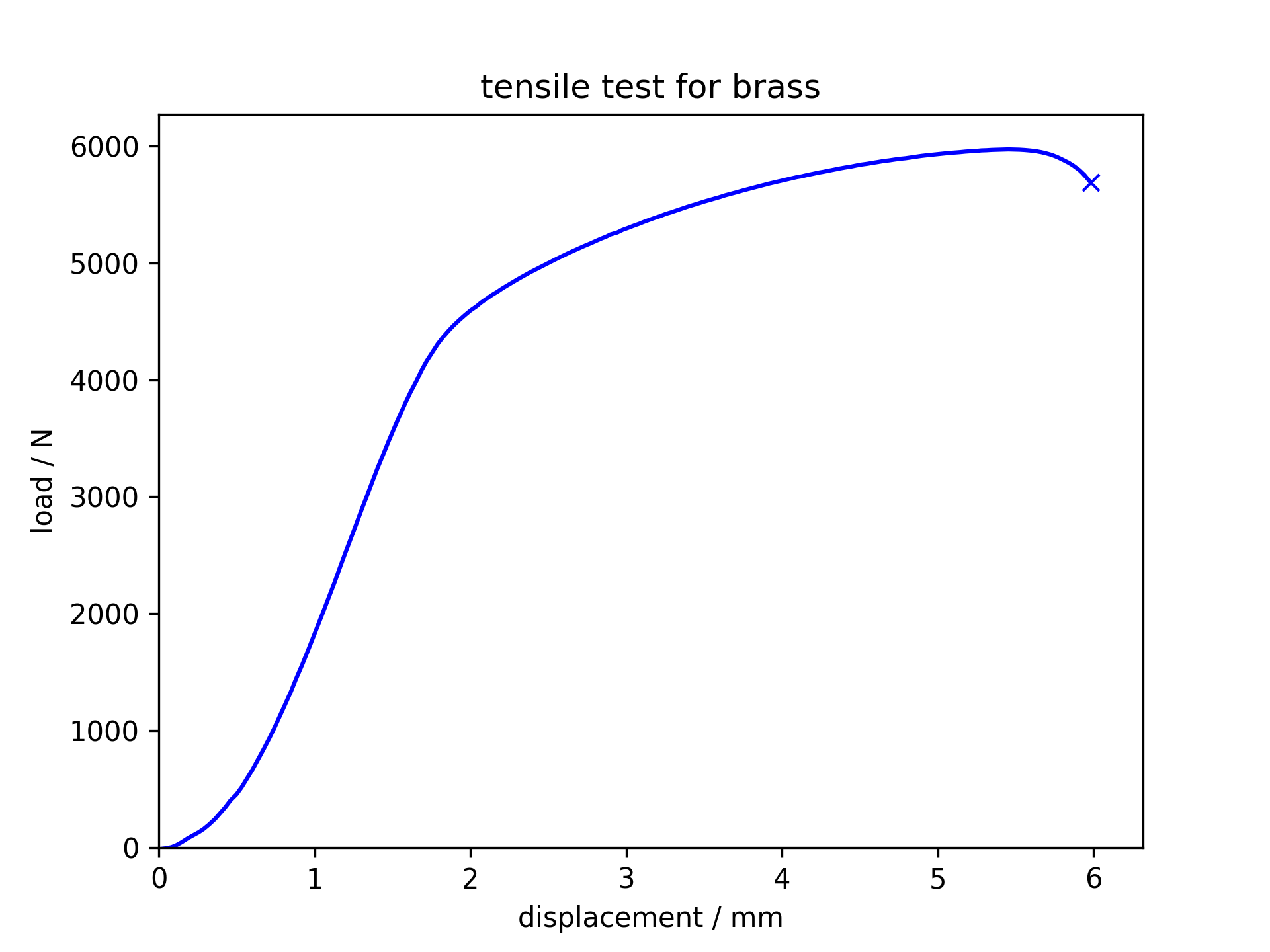
The brass is tougher
and can be stretched longer without failing. It is also more brittle
and does not neck significantly before fracture.
Tensile test for mild steel
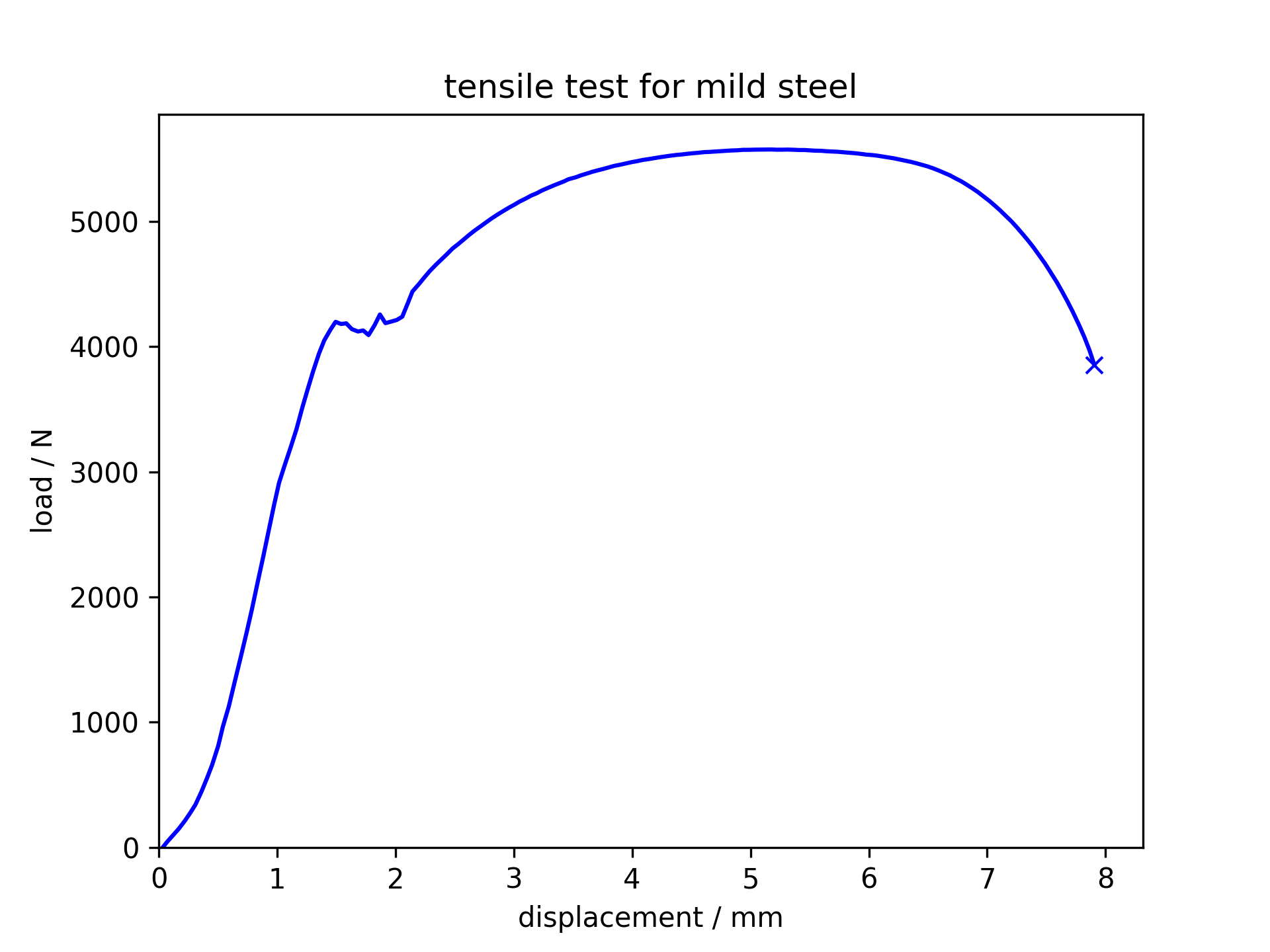
This low carbon
steel shows a pronounced drop in the stress required for plastic deformation
following initial yield. To learn the reasons behind this, click
.
Cottrell atmosphere
When the alloy is made,
at high temperatures allows the carbon solute atoms to diffuse towards the
dislocations where there is more open space.
This creates a Cottrell atmosphere along the length of a dislocation, which pins the dislocations, retarding their movement. This results in a higher initial yield stress.
After the dislocations escape from their Cottrell atmospheres, the yield stress drops.
This creates a Cottrell atmosphere along the length of a dislocation, which pins the dislocations, retarding their movement. This results in a higher initial yield stress.
After the dislocations escape from their Cottrell atmospheres, the yield stress drops.
The general increase in yield stress after the drop is due to work hardening
(see hardness section).
Tensile test for silver steel
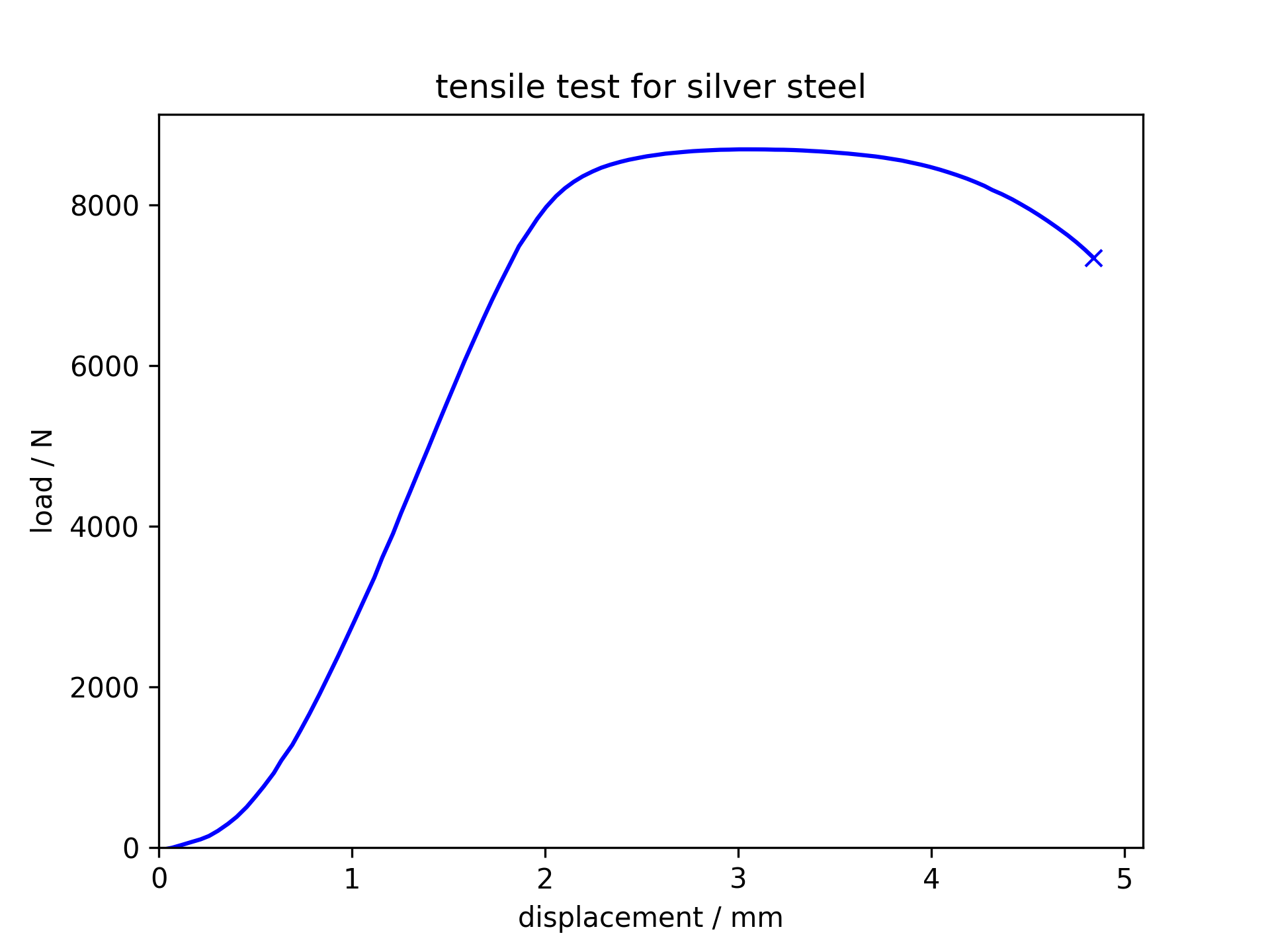
Silver steel is
more brittle than mild steel and undegoes less necking compared to mild
steel.
Tensile test for martensite
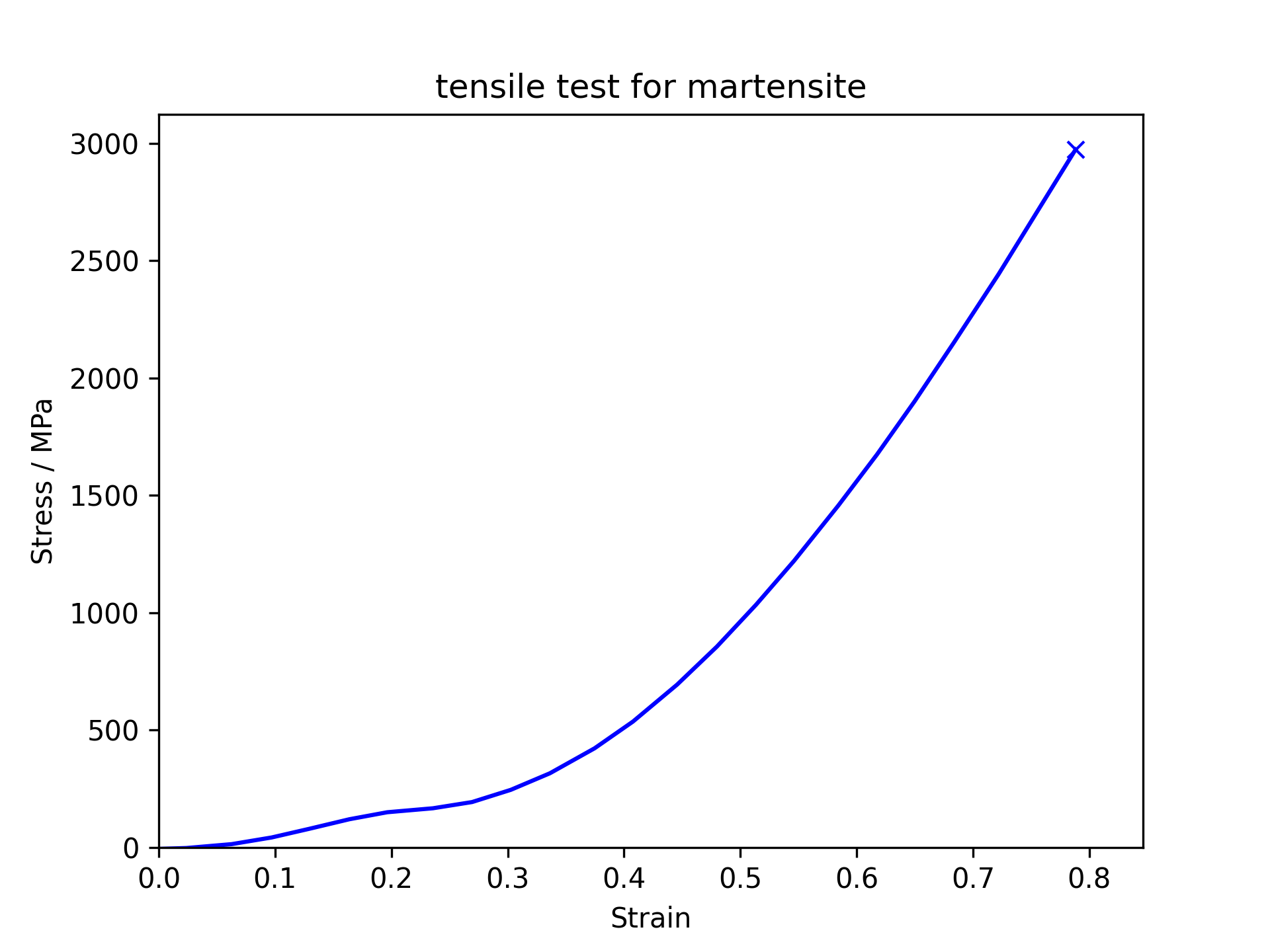
Martensite is very
brittle and hardly undergoes any plastic deformation before fracture.
Its yield stress is lower than silver steel as a result of residual
stress from quenching.
Tensile test for stainless steel
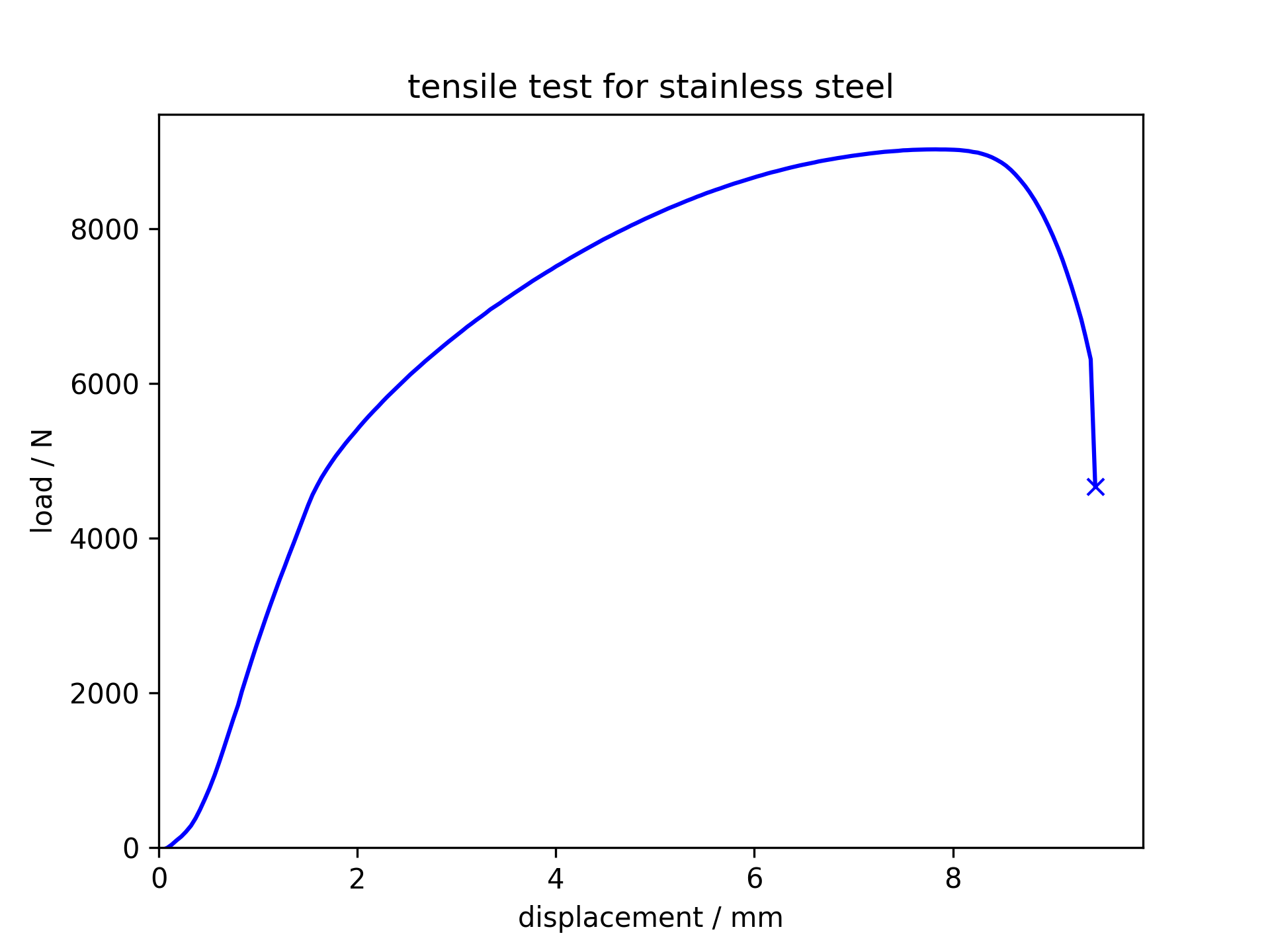
Stainless steel
is ductile and tough. It can be streched for a large length and absorb
a lot of energy before fracture. It also necks before fracture.
Load and displacement curves for different metallic samples
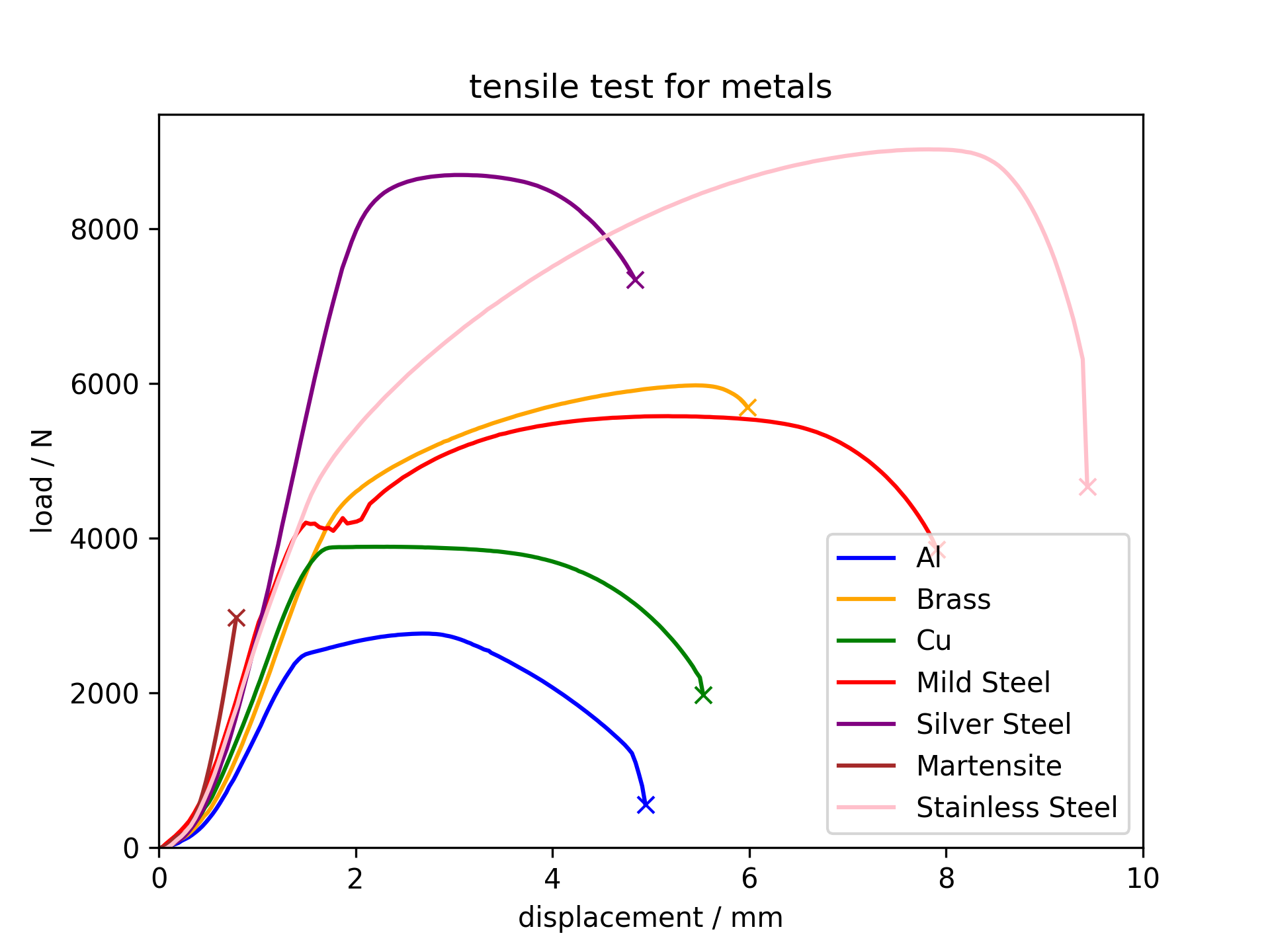
Stress and strain curves for different metallic samples