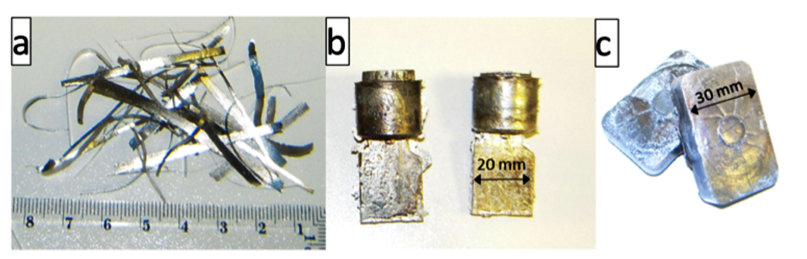
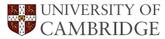
A steel with a chemical composition meant to form nanostructured bainite following appropriate heat treatment, was cooled rapidly from the liquid phase (1550 °C) using melt spinning and modified injection-suction methods, as well as from a semi-solid temperature (1430 °C) through thixoforming. The hardness of the as-cast melt-spun ribbons was about 900 HV due to a fine martensite-austenite mixture surrounded by 3-dimensional skeleton-like primary carbides of length scale 0.2-0.3 μm. The suction-injection cast method led to a similar structure but less hard (780 HV) due to a lower cooling rate. The thixoformed material showed unmelted globular fine grains and a eutectic mixture formed directly from the liquid phase. The variety of processed steel samples were tempered and their microstructures examined.
Materials Science and Technology (2016) https://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2016.1244141

| PT Group Home | Materials Algorithms |